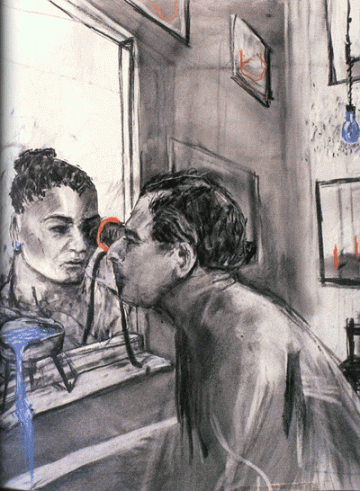Rest Energy, photo of a 1980 performance by Marina Abramovic and Ulay, photo from Galleria Lia Rumma
The Museum of Modern Art in New York currently hosts retrospectives of two idiosyncratic and uncompromising living artists, Yugoslavian born Marina Abramovic and South African William Kentridge. The two artists could hardly be more different from each other, but each has followed the path of art as something deeply personal and necessary.
Marina Abramovic emerged as a performance artist in the 1970’s. Using her own body as her medium, she explored the power of living presence in ritual acts of vulnerability and endurance. Her earliest works were so raw and risky they still shock – for example, in Rhythm 2 (1974), she took drugs that caused seizures, convulsions and catatonia. But then in the 70’s everyone was experimenting with drugs – she just did it in front of an audience.
In 1976 she began a twelve year collaboration with Ulay (Uwe Laysiepen). The work they did together achieved a kind of spiritual and aesthetic clarity that has not been surpassed, even as this kind of work has entered the mainstream with David Blaine‘s well-publicized acts of endurance. In “Rest Energy”, pictured at the top of the post, Abramovic and Ulay lean apart, their weight suspended by the tension of a bowstring with an arrow aimed at Abramovic’s heart.
Abramovic and Ulay traveled continuously, living in an old Citroen van (the van is in the MoMA exhibit), fully devoting their lives to their artistic experiment. A statement they wrote at the time (1975) reads:
ART VITAL
no fixed living-place
permanent movement
direct contact
local relation
self-selection
passing limitations
taking risks
mobile energy
no rehearsals
no predicted end
no repetition
extended vulnerability
exposure to chance
primary reactions
Abramovic and Ulay parted ways in 1988. Much of Abramovic’s solo work from the 90’s looks to me more strident and more self-conscious about making “statements”, but in her most recent work she seems to be rediscovering the power of simplicity.
The Abramovic retrospective at MoMA includes documentation of a great many of these performances that tested the limits of the mind and body and the relationship between artist and audience. It also includes living “reperformers”, re-enacting several of the most well-known actions. The one that has been most widely discussed is Imponderabilia, originally performed by Abramovic and Ulay in 1977. A naked male and female stand impassively facing each other in a narrow doorway, through which museumgoers may pass only by squeezing sideways between the pair.
Abramovic has long argued that performance art must be kept alive by reperformance, and in her 2005 show at the Guggenheim Museum she herself reperformed a number of seminal performance works originally done decades ago by such artists as Joseph Beuys and Valie Export. It is undeniable that the MoMA show is more interesting with live bodies interspersed among the old documentation, but the change of context has surely altered the effect of the pieces. It is not just that what were once radical experiments are now enshrined in the most institutional of museums. The original pieces were radically minimalist – highly clarified simple happenings in isolation, usually presented in blank gallery spaces. The MoMA exhibit is like a crowded menagerie of acts and images, with a steady flow of tourists trying to see it all before their feet give out or the kids start crying or they have to meet someone for dinner.
The title of the Abramovic show at MoMA is The Artist Is Present, and it is with her own simple presence that she makes the strongest statement and the deepest impression in this show. In the great atrium of the Museum, throughout the public hours while her exhibit is open, the 63-year-old artist sits silently at a table, while museumgoers are invited to sit directly across from her. She sits all day, and will do so for 77 days. This is about as radically minimal as performance can get. She is not doing anything sensational, really not doing anything at all. But if you’ve tried to sit still for even an hour you know it becomes incredibly grueling. You can often see the pain in her face as she holds steady eye contact with an endless stream of museum visitors, some of whom sit for moments, and some for hours. It is an act of extreme endurance, but also, in a way, an act of extreme generosity, giving herself to her audience in direct human presence. Observe for a while and you’ll see suffering, defiance, confrontation, resignation, engagement, boredom and bliss – the full range of the human condition living and breathing there before us. Amazingly, her simple presence fills up the gigantic atrium space more than any of the monumental pieces of art I’ve seen there over the years.
On the opening day, her former collaborator, Ulay, showed up at the table for an unexpected tearful reunion:

Ulay and Marina Abramovic, March, 2010, photo by Scott Rudd for MoMA
Just off the Atrium is the entrance to another immersive exhibit, William Kentridge: Five Themes. Timed to coincide with Kentridge’s multimedia staging of Shostakovich’s opera The Nose (based on Nikolai Gogol’s short story) at the Metropolitan Opera, this retrospective shows Kentridge’s drawings, prints, animated films, theatrical designs, optical experiments and even animatronic puppets as a diverse but highly unified body of work that spans media and obliterates the traditional line dividing graphic art and theatrical storytelling.
Kentridge became widely known in the 1990’s for his 9 Drawings for Projection (1989-2003), a series of richly evocative short animated films, made by drawing, erasing and redrawing large charcoal sketches on paper. Originally shown one at a time in galleries in conjuction with exhibits of the final-stage charcoal drawings, the series of films hangs loosely together as a single ongoing story. They tell of an industrialist, Soho Eckstein, his wife, and her lover, the bohemian Felix Teitlebaum, who is always depicted naked. Eckstein and Teitlebaum are opposites in a way, but both recognizably resemble Kentridge. The story in 9 Drawings plays out across the backdrop of the upheavals of South Africa in the late apartheid and early post-apartheid eras, but the films aren’t straightforwardly political. Instead they’re personal and poetic. The erasures and redrawing of the filmmaking technique, the transformations of the elemental and mechanical imagery, the ebb and flow of the lives of the characters, and the shifting sands of cultural change are all of a piece, an era of life experience distilled into a cinematic dream. I get the impression that the transformations of the drawings are not preconceived, but exploratory.
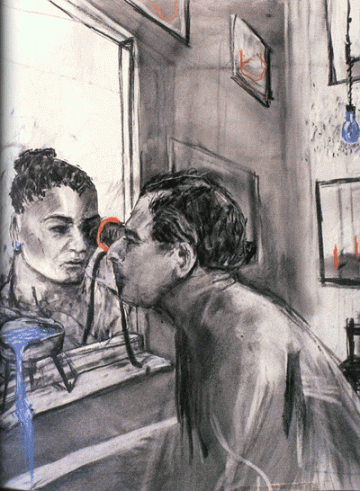
- Drawing from “Felix in Exile”, 1994, one of “9 Drawings for Projection” by William Kentridge
The museum show is arranged not chronologically or by media, but thematically. The 9 Drawings and other films are projected at monumental size, with the real drawings, also quite large, nearby, allowing one to experience the images in both their forms, as mutable projections and as the tactile reality of smudgy charcoal on heavily worked paper.
Kentridge is an obsessive drawer and mark-maker. One room in the MoMA show surrounds us with multiple projections showing him drawing, tearing paper, pouring ink, etc., often in reverse. Other rooms are filled with projections, drawings and objects based around designs for his recent operatic productions, Mozart’s Magic Flute and Shostakovich’s The Nose. There is almost too much to take in, a barrage of images and ideas, nearly all in bold black and white, with a rough, handmade texture. Throughout the exhibit there are many recurring images, including water and bathing, mechanically walking figures, birds and rhinoceroses, the industrialized landscape, Alfred Jarry’s corrupt king Ubu, and especially Kentridge’s own heavyset self-image.
Kentridge’s work is not colorful, and while it is bold, it is not simplistic. It is gray and ambiguous and conflicted. It draws upon the angular dynamism of early-20th-century avant-garde design, but the boldness is more than anything else the magnified theatrical gesture of the human form. This is the closest contemporary work I know to the great etchings of Goya, the Caprichos and the Disasters of War. For Kentridge the act of drawing is theatrical, improvisational and demonstrative, and theater is a graphic art where shadows and lines convey ideas and feelings.

Drawing for II Sole 24 Ore (World Walking), 2007, by William Kentridge; Charcoal, gouache, pastel, and colored pencil on paper, Marion Goodman Gallery
I’ll close with a quote from the Phaidon Monograph, William Kentridge, by Carolyn Christov-Bakargiev et al, that reveals something about his open-ended creative process:
“Drawing for me is about fluidity. There may be a vague sense of what you’re going to draw but things occur during the process that may modify, consolidate or shed doubts on what you know. So drawing is a testing of ideas; a slow-motion version of thought. It does not arrive instantly like a photograph. The uncertain and imprecise way of constructing a drawing is sometimes a model of how to construct meaning. What ends in clarity does not begin that way.”
Marina Abramovic: The Artist Is Present, organized by Klaus Biesenbach, Chief Curator at Large, The Museum of Modern Art, and Director, P.S.1 Contemporary Art Center, is on view through May 31, 2010, at the Museum of Modern Art, New York.
William Kentridge: Five Themes, originally organized for the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art and the Norton Museum of Art by Mark Rosenthal, is on view through May 17, 2010 at the Museum of Modern Art, New York.
Images in this post link back to the sites where I found them.